
Privacy Policy
Your privacy is important to us at STAAR Surgical Company and our global subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively, "STAAR" or “we”). Responsibility lies with STAAR US (25510 Commercentre Drive, Ste. 200, Lake Forest, California 92630 U.S.A.) and/or one of its subsidiaries listed in the Annex attached at the end of this document. The individual responsible depends on which of the STAAR entities listed in the Annex processes your personal data as a controlleri.
This Privacy Policy ("Policy") applies to STAAR websites, and any mobile applications ("Apps") and digital platforms and services ("Services") (collectively, "Sites")..where STAAR is acting as a data controller, and explains how we collect, use, disclose and otherwise process information that identifies you or from which you are identifiable (“Personal Information”). It also applies to personal information STAAR may otherwise collect: (i) through our products and services; (ii) when you interact with us by means other than a STAAR Internet Site or App, for example, in person, by telephone, or at a trade show or training; and (iii) from our customers, distributors, suppliers, vendors, and other business partners (collectively “Business Partners”). Please be sure to read this entire Policy before using or submitting information to our Sites, or to your health care provider for purposes of ordering STAAR products on your behalf.
Personal Information Collected
We collect information from you in various ways when you use our Sites. We may collect Personal Information you directly provide on our Sites, such as name, email, age, contact information and refractive disorder (e.g., nearsightedness) or Personal Information you generate as a user of our Sites. If you are a patient of one of our customers, a healthcare professional or an institutional healthcare provider (collectively, "Providers"), they may provide identifying information as part of ordering your implantable lenses, such as name and date of birth, along with vision and eye measurements necessary to identify appropriate implant options for each case. STAAR strongly discourages Providers against providing patient names.
If you are a Provider, you are responsible for providing adequate notice to, and obtaining any legally required authorization, consent or other permission from your patients prior to providing their Personal Information to STAAR through the Sites (though STAAR does not request patient Personal Information). By submitting any Personal Information about a patient to STAAR, you represent and warrant to STAAR that you have provided adequate notice to and obtained all required consents from patients to do so.
Where we collect and process Personal Information about your health or medical status (i.e., “Sensitive Personal Information”), this information may be subject to stricter requirements than other Personal Information. Sensitive Personal Information we may collect includes name and date of birth in connection with vision and related health information. Before providing (or consenting to the disclosure of) Sensitive Personal Information to us, we urge you to carefully consider whether or not to disclose such information.
In addition, some information may be automatically collected when you visit our Sites – please see the “Cookie Policy” Section below.
Interactive Services
If you choose to participate in our questionnaires and surveys and other Interactive Services, we will collect Personal Information that you disclose, to help us better understand how STAAR products are used and results achieved by patients.
The information you provide through Interactive Services may be combined (subject to all applicable laws) with the Personal Information provided elsewhere in or through the Services. We may combine your and others' Personal Information to create summary data that we will use for our business purposes, such as research to improve our products and analyses that may help us better market our products.
If you submit Sensitive Personal Information (e.g., identifiable health-related information) through the Services to participate in a clinical trial, referral program or otherwise, we may use such Sensitive Personal Information to assess whether you qualify for enrollment or participation, to contact you about potential participation, and to provide you with additional information.
You may provide information to be published or displayed ("Posted") on public areas of the Sites (collectively, "User Contributions"). If you Post User Contributions, then you do so at your own risk. STAAR does not control the actions of third parties with access to your User Contributions.
Cookie Policy
In line with legal requirements, we may collect certain information through the use of "cookies." Cookies are small data files that are stored on your hard drive by a website, which the site may then use to identify you on your next visit. Among other things, the use of cookies helps us to improve our Sites and your experience. Where allowed we use cookies to see which areas and features are most popular, to count the number of computers accessing our Sites, to personalize your experience, and to remember your preferences.
A "web beacon" is a piece of code that enables us to monitor user activity and website traffic. A "cookie" is a randomly-generated unique numeric code stored in the user's web browser settings or computer's hard drive. A cookie typically contains the name of the domain (internet location) from which the cookie originated, the "lifetime" of the cookie (i.e., when it expires), as well as the randomly generated unique numeric code.
We link the information we store in cookies to any personally identifiable information you submit while on our Sites when in line with your local law. If you prefer not to receive cookies on this website, you can set your preferences in the cookie banner to reject non-essential cookies. If you do so however, you may not be able to access some of the features or services of our Sites. We may track your activities over time and across third-party websites, apps or other online services to display advertisements on third-party websites. If you do not want us to use your information in this way, please see "Your Privacy Choices" below. For more information about our digital advertising practices, please see "Digital Advertising" below.
If our third party vendors, consultants and other service providers ("Service Providers") use cookies, their use is not covered by this privacy Policy. We do not have access or control over those cookies. Our Service Providers use session ID cookies to collect data in order to enable us to provide a better user experience.
Google, as a third party vendor, uses cookies to serve ads. Google's use of the first party cookies (such as Google Analytics cookies) and third-party cookies (such as the DoubleClick cookie) enables it to serve ads to you based on your visit to our Sites and other sites on the Internet. Additionally, these cookies are used to generate a report on how our ad impressions, other uses of ad services, and interactions with these ad impressions and ad services are related to visits to our Sites. Users will be asked for consent where legally required - if not – users may opt out of the use of the cookie by visiting the Google ad and content network privacy Policy here: adssettings.google.com or http://optout.networkadvertising.org/#!/.
With your consent, we use pixels on our Sites to track visits to and interactions with the site and to analyze the content a user has viewed when visiting the site (e.g., EVO Visian ICL® videos on discovericl.com) in order to measure, optimize and improve the content of the site. The Meta and Tik Tok Pixels record information about a Facebook/TikTok user's session on our Sites, which it sends to the parent companies, along with an anonymised version of the user’s Facebook/TikTok ID. We collect and store information gathered from the session the Pixel cookie for 180 days. You can delete the Pixel cookies and other cookies at any time by clearing your browser cache. For further information about these Pixels please see: https://en-gb.facebook.com/business/help/651294705016616 and https://ads.tiktok.com/help/article/tiktok-pixel.
Taboola and Criteo Pixels report what actions you have taken on our Sites, and possibly identifying data. These pixel tags are used in combination with cookies to generate analytics on the actions of visitors on our Sites. The following data may be processed: events on our Sites, including initial and subsequent page visits, transaction data, the user’s gender (if provided) and information about the user’s browser read from the user agent, include operating system, browser type, browser version and associated IP address (which is shortened after 30 days so no further location accuracy can be determined). More information on how these vendors manage user information, and what you can do to opt out/disable pixels, can be found on Taboola’s and Criteo’s respective privacy policies.
Connecting with Social Media through the Services Certain Services may link with social media platforms and social media plug-ins (e.g., the Facebook "Like" button, "Share to Twitter" button) (collectively, "Social Media") when consent was given. When accessing the Services through a Facebook or other Social Media account, STAAR may (depending on the applicable user privacy settings) automatically have access to information provided to or through the Social Media platform. STAAR may collect and use this information for the purposes described in this Privacy Policy or at the time the information was collected.
Connecting with Social Media through Service Providers Third parties that assist us with our business operations also collect and use information (including Personal Information and "Usage Data" (i.e., information about an individual's activity on or through the Services that, by itself, does not identify the individual, such as browser type, operating system and webpages visited)) through the Services and also may share the collected information with us. For example, our vendors collect and share information with us to analyze use of the Services, to help us detect and prevent fraud and to improve user experience.
We use cookie consent banners on our Sites to provide you the option to personalize your user experience and maintain regulatory requirements on data collection, opt-in/out, pixel tracking, etc. You will be asked to customize your preference the first time you use a Site, and may update those preferences anytime thereafter by clicking the “Cookie Settings” box at the bottom of the screen.
Use of your Personal Information You are not required to provide us with your Personal Information, however, if you choose not to provide us with your Personal Information, you may not be able to fully utilize our Sites. We use your Personal Information as necessary to perform a contract (e.g., to respond to your enquiries, to register you for an account with us, to provide you and your Provider with our Services), to comply with a legal obligation (e.g., for fraud and security monitoring purposes and regulatory compliance), for reasons of public interest in the area of public health (e.g., for our medical device vigilance obligations) or for our legitimate business interests unless consent is a legal requirement (e.g., to operate and improve our Sites, develop and improve our products, to send you messages, and for other purposes described in this Privacy Policy or disclosed to you on our Sites or in connection with our Services). For example, we may use the information we collect from you on our Sites:
- to personalize and improve your experience on our Sites;
- to respond to comments and questions and provide customer service;
- to deliver service messages and other services and content you request and to send information related to accounts and services, including confirmations, invoices, technical notices, updates, security alerts, and support and administrative messages;
- to send you information about promotions, products, and services offered by STAAR and our selected partners;
- to conduct an aggregated analysis of the performance of promotions; and
- to use Remarketing with Google Analytics to advertise online.
Exercising Your Privacy Rights. Depending on where you reside, you may have the following rights in relation to your Personal Information:
- Right to access (i) the categories of information collected by us about consumers and/or shared with third parties (set forth in this Policy); and (ii) your Personal Information collected by us
- Right to correct inaccurate or outdated Personal Information
- Right to delete, subject to certain exceptions
- Right to opt out of certain processing
- Right to portability/right to request your Personal Information provided to you in a common file format (e.g., .pdf, .xlsx)
- Right to opt out of the sale of your Personal Information to third parties
- If your Personal Information changes, we invite you to correct or update your information as soon as possible. You can request changes, access to your information or exercise other privacy rights by emailing: privacyoffice@staar.com or calling 888.909.0123.
Depending on the type of request you make, we may require you to provide additional information about yourself as part of our identity verification process. STAAR will inform you of the specific information it requires (if any) to verify your identity after it receives your request. Once we are able to validate your identity, we will respond to your request in a timely manner (as set forth in applicable legal requirements).
Please note that we may deny a deletion request in whole or in part if retaining your Personal Information is necessary for us or our service providers to (1) complete the transaction for which we collected the Personal Information, provide the product requested by your Provider, or otherwise perform a contract with you/your Provider; (2) detect security incidents, protect against deceptive, fraudulent or illegal activity (or prosecute those responsible for such activities); (3) comply with legal obligations; (4) engage in scientific, historical or statistical research in the public interest where such deletion may render impossible or seriously impair the research’s achievement, if you previously provided informed consent; or (5) make other internal and lawful uses of that information that are compatible with the context in which data was provided, or as otherwise permitted under applicable law.
Sharing of Personal Information We may share information, including Personal Information, with our third party service providers to perform the functions for which we engage them, such as communications platforms supporting EVO ICL Advisor and STAAR mobile applications (e.g., EVO ICL Consultation App), administrative cloud services (e.g. Office365), data analysis, system design and maintenance, customer services, cybersecurity, order fulfillment and billing, and for marketing and promotions. We may also share Personal Information with third parties to (a) comply with laws or respond to lawful requests and legal process, (b) protect the rights and property of STAAR, our agents, members, and others including to enforce our agreements, policies and terms of use, (c) respond to an emergency or protect the personal safety of any person in the good faith belief that disclosure is needed for that purpose; or (d) in connection with any merger, sale of company assets, financing, or acquisition of all or a portion of our business to another company. In any such event, we will provide notice if your data is transferred and becomes subject to a different company’s privacy policy.
Social Media Plugins When you use the Services, Social Media operators can place a cookie on your computer to recognize individuals who have previously visited the Services. If you are logged into a Social Media account while using the Services, the social plugins allow that Social Media operator to receive information that you have accessed and used the Services. The social plugins also allow the Social Media operator to share information about your activities in or through the Services with other Social Media users. For example, Facebook Social Plugins allows Facebook to show your Likes and comments on our pages to your Facebook friends. Facebook Social Plugins also allows you to see your friends’ Facebook activity through the Services. STAAR does not control any of the content from the Social Media plugins. For more information about Social Media plugins, please refer to the privacy policies and other legal notices of the Social Media platform.
Digital Advertising If you consent to receive marketing communications, we use third-party advertising companies to serve ads on other websites and digital services. These companies may use information obtained from data collection tools to measure advertising effectiveness and to provide advertisements of interest to you. You can opt out here so as not to receive targeted ads from use of the tools, but this will not affect any general advertisements you may receive.
Security and Retention of Your Personal Information STAAR takes reasonable security measures to protect your personal information to prevent loss, misuse, unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, and destruction. Please be aware, however, that despite our efforts, no security measures are impenetrable. If you use a password on our Site, you are responsible for keeping it confidential. Do not share it with any other person. If you believe your password has been misused, please advise us immediately.
We retain information as long as it is necessary and relevant for our operations. In addition, we retain Personal Information to comply with applicable laws, regulatory requirements, prevent fraud, resolve disputes, troubleshoot problems, assist with any investigation, enforce our Terms of Service, and other actions. When STAAR no longer needs your Personal Information for our business or legal retention purposes, we dispose of it. The criteria used to determine the retention periods include: (i) how long the Personal Information is needed to provide the Services and operate the business; (ii) the type of Personal Information collected; and (iii) whether we are subject to a legal, contractual or similar obligations to retain the Personal Information (e.g., mandatory data retention laws, government orders to preserve data relevant to an investigation, or data that must be retained for the purposes of litigation or disputes). We reserve the right to de-identify and retain information for security analytics, research, development or other legitimate purposes.
We employ security measures intended to help protect the security of all information submitted through the Services. The security of information transmitted through the internet cannot, however, be guaranteed. We are not responsible for any interception or interruption of any communications or for changes to or losses of data through the internet. Users of the Services are responsible for maintaining the security of any password, user ID or other form of authentication involved in obtaining access to password protected or secure areas of the Services. Any access to the Services through your user ID and password will be treated as authorized by you. To help protect your Personal Information, we may suspend your use of all or part of the Services, without notice, if STAAR suspects or detects any breach of security. Unauthorized access to such areas is prohibited and may lead to criminal prosecution.
Your Privacy Choices You may “opt-out” of receiving promotional emails from STAAR by following the instructions in those emails or by deleting STAAR mobile apps (in Settings). You may also send requests relating to promotional messages and your permission for sharing information with third parties for their marketing purposes by emailing a detailed request to privacyoffice@staar.com. Opt-out requests will not apply to transactional service messages, including messages about any current STAAR account or Services. You may “opt-out” of providing requested information on Sites, but then you may not be able to use the Site as intended.
Withdrawing Consent Where we rely on your consent to process your Personal Information, you may withdraw your consent at any time by opting out (as described above) or providing a detailed request to privacyoffice@staar.com. The withdrawal of consent shall not affect the lawfulness of processing based on consent before its withdrawal.
Do Not Sell/Share Personal Information STAAR does not and will not sell Personal Information provided by users of our Sites, including but not limited to any information about minors.
California Privacy Rights The California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (“CCPA”) provides certain rights to users of our Sites and others who reside in the State of California (“CA Consumers”). Below is a description of STAAR’s practices regarding the collection, use and disclosure of personal information regarding CA Consumers and of CA Consumers’ rights concerning their personal information.
CA Consumers have the right to request that STAAR disclose what Personal Information it collects, uses, discloses and sells. Specifically, a CA Consumer may request details concerning any or all of the following: (i) specific pieces of personal information that STAAR has about the CA Consumer; (ii) categories of personal information STAAR has collected about the CA Consumer; (iii) categories of sources from which the personal information is collected; (iv) categories of personal information about the CA Consumer that STAAR sold or disclosed for a business purpose; (v) categories of third parties to whom the personal information was sold or disclosed for a business purpose; and (vi) the business or commercial purpose for collecting or selling personal information. STAAR does not sell Personal Information collected from users of its Sites.
Table 1 describes the categories of CA Consumers’ personal information STAAR has collected in the last 12 months, categories of sources from which that information was collected, the business or commercial purpose for which the information was collected, and the categories of third parties with whom STAAR shares such personal information:
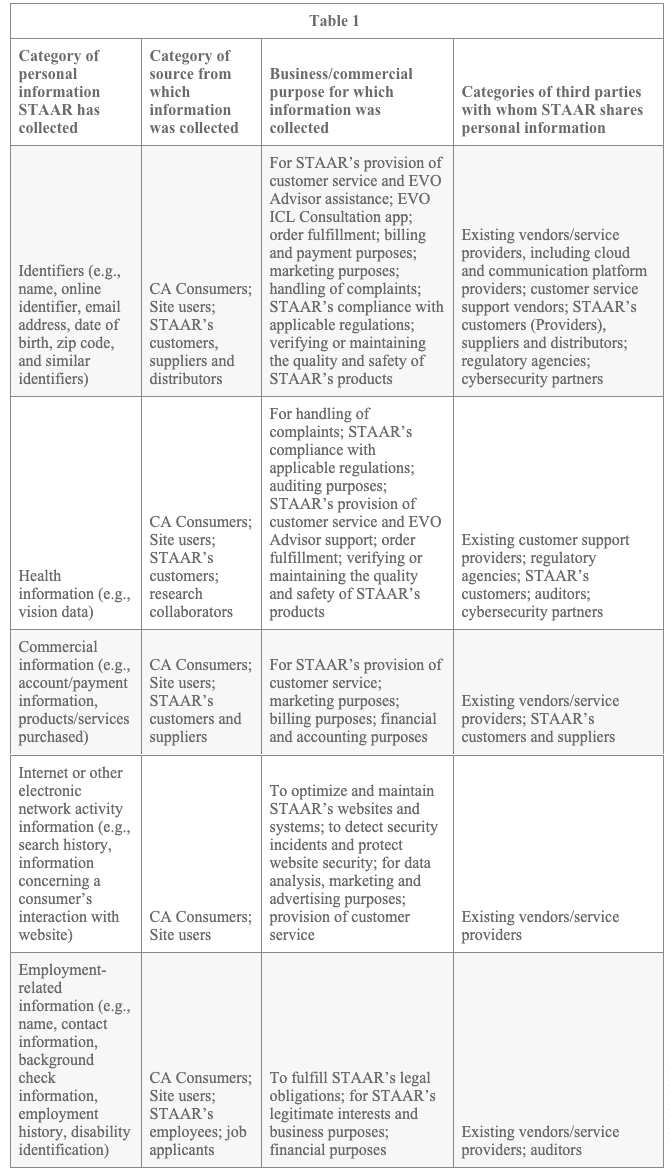
In the last 12 months, STAAR has disclosed all of the categories of personal information included in Table 1 (i.e., identifiers, health information, commercial information, internet or other electronic network activity information, and employment-related information) to third parties for a business or commercial purpose.
CA Consumers have the right to request the deletion of their personal information which is collected or maintained by STAAR (subject to exceptions)opt out of sale/sharing of Personal Information, correct inaccurate Personal Information, limit use of sensitive Personal Information, and opt-out of automated decision-making. See the “Exercising Your Privacy Rights” section above for information on how to exercise these options.
CA Consumers also have the right to opt out of the sale of their Personal Information and avoid discriminatory treatment for the exercise of privacy rights conferred by the CCPA. STAAR does not sell Personal Information and will not discriminate or retaliate against any CA Consumer for his/her exercise of those rights.
A CA Consumer may use an authorized agent (which may be another person or a business entity registered with the CA Secretary of State) to submit any of the requests described above on the CA Consumer’s behalf. The authorized agent should follow processes specified above for submitting such requests. When a CA Consumer uses an agent to submit a request, STAAR may require the CA Consumer to provide the agent with written permission to do so and may also require the CA Consumer to verify his/her own identity directly with STAAR. STAAR may deny a request from an agent that does not submit proof that the agent has been authorized by the CA Consumer to act on the CA Consumer’s behalf.
CA Consumers may contact STAAR with questions or concerns about STAAR’s privacy policies or practices. Please see the section below (“Contact Us”) for STAAR’s contact information. CA Consumers can also find out more information on their privacy rights, and file complaints, with the California Attorney General or California Privacy Protection Agency.
Users in the European Union (EU/EEA), United Kingdom (UK) and Switzerland (CH). The following terms (in addition to all other terms in this Privacy Policy) apply to users in the EEA, UK and CH.
Your Rights Individuals in the EU, UK and Switzerland have certain data subject rights which may be subject to limitations and/or restrictions. These rights include the: (i) right to request access to and rectification or erasure of their Personal Information; (ii) right to request restriction of processing or to object to processing of their Personal Information; (iii) right to ask for a copy of their Personal Information to be provided to them, or a third party, in a digital format (data portability); and (iv) right to file a complaint with a data protection authority. Individuals also have the right to withdraw consent for the processing of their Personal Information at any time, however, such withdrawal will not affect the lawfulness of processing of Personal Information that (a) occurred prior to the consent being withdrawn; or (b) is processed under a different legal basis (e.g., legal or contractual compliance). Please note, however, that we reserve the right to enforce statutory restrictions on our part, for example if we are obliged to retain or process certain data, have an overriding interest (insofar as we may invoke such interests) or need the data for asserting claims. If exercising certain rights will incur costs on you, we will notify you thereof in advance. Consent given can be withdrawn at any time, but this does not affect data processed prior to withdrawal. Please further note that the exercise of these rights may be in conflict with contractual obligations and this may result in consequences such as premature contract termination or involve costs. If this is the case, we will inform you in advance unless it has already been contractually agreed upon.
If individuals want to exercise any of their rights, they can contact us at privacyoffice@staar.com or the local data representatives as provided in the “Identity of Controller” section. In general, exercising these rights requires that you are able to prove your identity (e.g., by a copy of identification documents where your identity is not evident otherwise or can be verified in another way). Individuals also have the right to enforce his/her/their rights in court or to lodge a complaint about the processing of their Personal Information with their local data protection authority.
Privacy Policies of Third Parties This Privacy Policy only addresses the use and disclosure of information by STAAR. We may provide links to outside websites or advertisements for third parties that have their own privacy policies and data collection, use and disclosure practices. Our business partners have their own privacy policies too. We encourage you to familiarize yourself with the privacy Policies provided by all third parties prior to providing them with information or taking advantage of an offer or promotion.
International transfers of Personal Information STAAR Surgical Company, the manufacturer of implantable lenses for the eye and companion delivery systems (“Products”), has headquarters located in the United States (US) and international operations in Switzerland (STAAR Surgical AG). Your Personal Information may be accessed or transferred to STAAR Surgical AG and/or STAAR Surgical Company, or our sub processors in the US or other countries, for the purposes outlined in this Policy. By providing us with your Personal Information, you consent to this transfer although your country may not consider it to provide for adequate privacy protections. Data transfers to bodies in states outside the European Union (EU) will take place to the extent that you have given your consent, and/or we ensure that appropriate safeguards are implemented to provide an adequate level of data protection such as standard contractual clauses approved by the European Commission or adequacy decision by the European Commission.
Data Privacy Framework On 10 July 2023, the European Commission adopted its adequacy decision for the EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework (“DPF”). STAAR adheres to the EU-U.S. DPF Principles with regard to personal data transferred from the European Union and the United Kingdom and the Swiss-U.S. DPF Principles with regard to personal data transferred from Switzerland. For more information, see STAAR’s Data Privacy Framework Addendum. In keeping with DPF Principles, we will always take reasonable measures to protect the privacy and security of your Personal Information as expressed in this Policy, regardless of where it is processed or stored.
For sub-processors located in a country without adequate statutory data protection, we require the recipient to undertake to comply with data protection (for this purpose, we use the revised European Commission’s standard contractual clauses, which can be accessed here), unless the recipient is subject to a legally accepted set of rules to ensure data protection and unless we cannot rely on an exception. An exception may apply for example in case of legal proceedings abroad, but also in cases of overriding public interest or if the performance of a contract requires disclosure, if you have consented or if data has been made available generally by you and you have not objected against the processing.
Identity of the Controller
For purposes of EU, UK and Swiss data protection laws (GDPR, DSG, and revDSG), the data controller (i.e. the organization that determines the purposes and means of processing) for the Personal Information that you submit to our Sites is STAAR Surgical AG (“STAAR CH”). For purposes of U.S. privacy laws, the data controller is STAAR Surgical Company (“STAAR US”). Please see the Contact Us information below for the details for the data protection representative for each entity.
Contact Us:
STAAR US and STAAR CH have appointed STAAR Surgical AG Niederlassung Germany (“STAAR DE”), Harksheider Str. 3, 22399 Hamburg, Germany, Email: DPRepresentative@staar.com, as the data protection representative in Europe. The data protection officer for STAAR DE is IITR Datenschutz GmbH, Marienplatz 2, 80331 München, Email: email@iitr.de.
STAAR US and STAAR CH have appointed STAAR Surgical UK, Ltd. (STAAR UK), Suite 2, The Granary, 50 Barton Road, Worsley, Manchester, United Kingdom M28 2EB, Email: privacyoffice@staar.com, as the data protection representative in the UK.
STAAR US has appointed STAAR Surgical AG, Hauptstrasse 104, CH – 2560 Nidau, Switzerland, Email: DPRepresentative@staar.com, Phone: +41 32 332 88 88, as the data protection representative in Switzerland.
The data protection representative for STAAR US and STAAR UK is Kathleen Determann, 25510 Commercentre Drive, Ste. 200, Lake Forest, CA 92630, Phone: 1.626.303.7902, Email: PrivacyOffice@staar.com.
For all other STAAR organizations globally (i.e., outside the EU, UK and CH), STAAR’s relevant local entity is the data controller and data protection representative for STAAR US and STAAR CH. In some cases, you will need to contact the local distributor (as data controller) to exercise your privacy rights as STAAR discourages distributors from sharing Personal Information. Contact information for all distributors and subsidiaries is available at http://www.staar.com/distributors-list.
STAAR’s uses and shares your personal information (i) based on your consent, (ii) as needed to comply with applicable law or performance of a contract, (iii) as needed for the performance of tasks in the public interest in the area of public health, (iv) as necessary for pursuing STAAR’s legitimate interests, such as ensuring its network and information security, preventing fraud, and for its direct marketing activities, and (v) as necessary for the establishment, exercise or defense of legal claims.
Children’s Privacy The Sites are not intended to attract children, and we do not knowingly collect any Personal Information of anyone under the age of 13. If you believe your child is using our Sites, please contact us at privacyoffice@staar.com so we can investigate and delete any inappropriate information.
Testimonials We post customer testimonials on our websites which may contain Personal Information. We do obtain the customer’s consent via email prior to posting the testimonial to post their name along with their testimonial. If you wish to request that your testimonial be removed, you may do so by emailing us at privacyoffice@staar.com.
Public Forums Our website offers publicly accessible blogs or community forums. You should be aware that any information you provide in these areas may be read, collected, and used by others who access them. To request removal of your Personal Information from our blog or community forum, contact us at privacyoffice@staar.com. In some cases, we may not be able to remove your Personal Information, in which case we will let you know if we are unable to do so and why.
Medical Education and Webinars For those health care providers who share their Personal Information as part of a medical education program, STAAR will use that information solely for such educational purposes unless you provide express consent to receive marketing information. STAAR will share your information with third parties for the purposes of attending webinars and/or making travel and accommodation arrangement.
Changes to This Policy STAAR may change this Policy from time to time, including using collected information for new, unanticipated uses not previously disclosed. If we make any changes to this Policy to reflect changes in collection or dissemination of information, we will change the "Last Updated" date above. We encourage you to review this Policy whenever you visit our Sites to understand how your Personal Information is used.
Job Applicants If you have applied for employment with STAAR or one of its affiliates, the Personal Information submitted with your job application will be used to process and consider your job application and where in our legitimate interest for business management purposes. STAAR will not sell the information on your application to unaffiliated third parties for their marketing purposes. We may share the information on your applications with recruiters, consultants, attorneys, background services and our affiliates. The information on your application may also be used for certain regulatory, compliance and legal purposes, consistent with this Policy. Should we enter into an employment contract with you, we will provide further notification to you about the processing of your Personal Information as an employee. If you have questions or requests concerning our use of your Personal Information, please provide a detailed request to privacyoffice@staar.com. In most cases, your Personal Information entered into a third party recruiting platform will be subject to that vendor’s privacy policy available on their site.
Employees Employee Privacy Notices are made available to STAAR employees upon hire, and copies can be found in your training documentation and on the STAAR intranet (Corporate Policies). Any questions should be directed to your Human Resources partner.
STAAR Website Privacy Policy Annex
List of relevant STAAR entities:
- STAAR Surgical Company (Delaware, United States)
- STAAR Surgical UK, Ltd. (Manchester, England)
- STAAR India Pvt. Ltd (Delhi, India)
- STAAR Surgical AG (Nidau, Switzerland)
- STAAR Surgical AG Niederlassung Deutschland (Hamburg, Germany)
- STAAR Surgical AG Sucursal Espaňa (Barcelona, Spain)
- STAAR Surgical Japan (Tokyo, Japan)
- STAAR Surgical Pte. Ltd. (Singapore)
주요 안전성 정보
ICL은 성인을 대상으로 -0.5D에서 -18.0D 범위의 근시와 6.0D까지의 난시 교정에 대해 승인되었습니다. 21세에서 60세 사이의 성인이 ICL 수술 대상이 됩니다. 안내렌즈삽입술의 성공적인 결과를 위해서는 지난 1년간 시력에 변화가 없어야 합니다. ICL 수술은 안경 및 콘택트렌즈 사용이 필요하지 않도록 시력을 교정합니다. 눈의 노화로 인해 자연적으로 필요한 돋보기 안경은 ICL 안내렌즈삽입술을 받은 후에도 필요할 수 있습니다. ICL은 라식(LASIK), 굴절교정레이저각막절제술(PRK) 및 절개 수술을 포함한 다른 굴절 교정수술법들과 콘택트렌즈 및 안경 등의 시력 교정 방법에 대한 대안이 될 수 있습니다. ICL 안내렌즈삽입술은 외과적 수술이므로 심각한 부작용을 유발할 수도 있습니다. 일반적인 굴절 교정 수술과 관련하여 보고된 발생 가능한 부작용 및 합병증에는 추가적 수술, 백내장 발생, 최대교정시력 손실, 안압 증가, 각막내피세포 손실, 결막 자극, 급성 각막 부종, 지속적 각막 부종, 안내염, 빛번짐, 눈부심, 전방출혈(안구 내 출혈), 전방 축농(안구 내 고름), 염증, 렌즈 탈구, 황반 부종, 동공 무반응, 동공차단 녹내장, 심각한 안내 염증, 홍채염, 포도막염, 유리체 손실 및 각막 이식 등이 있습니다. ICL 수술을 고려하기 전, 정밀 눈 검사를 받은 후 안과 전문의에게 ICL 수술의 장점, 위험요소 및 부작용에 대해 상담 하십시오. 수술 후 회복을 위한 시간에 대해서도 상담하십시오.
국가 또는 지역 선택
Latin America
참고자료
Home - 광고심의필: 조합-2022-04-030 (유효기간: 2025.02.07)
1. Gonzalo Carracedo, et al. The role of dinucleoside polyphosphates on the ocular surface and other eye structures. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016 Nov;55:182-205. 2. Paul J Dougherty, et al. Refractive outcomes and safety of the implantable collamer lens in young low-to-moderate myopes. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017;11:273–277. 3. Gregory D. Parkhurst, et al. Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantation in United States Military Warfighters: A Retrospective Analysis of Early Clinical Outcomes of the EVO ICL. J Refract Surg. 2011;27(7);473-481. 4. Feingold et al. Biocompatible, optically transparent, ultraviolet light absorbing, polymeric material based upon collagen and method of making. USPTO June 8, 1999. 5. ICL in Treatment of Myopia (ITM) Study Group. Postoperative Inflammation after Implantation of the Implantable Contact Lens. Ophthalmology 2003;110:2335-2341. 6. Steven Schallhorn, MD et al. Night Driving Simulation in a Randomized Prospective Comparison of Visian Toric Implantable Collamer Lenses and Conventional PRK for Moderate to High Myopic Astigmatism. Journal of Refractive Surgery Vol.26, No. 5, 2010:321-326 7. Gregory D Parkhurst. A prospective comparison of phakic collamer lenses and wavefront-optimized laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis for correction of myopia. Clinical Ophthalmology 2016;10:1209-1215. 8. Donald R Sanders et al. United States Food and Drug Administration Clinical Trial of the Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL) for Moderate to High Myopia Three-Year Follow-up. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:1683–1692. 9. Elena Martines-plaze, et al. Effect of the EVO + Visian Phakic Implantable Collamer Lens on Visual Performance and Quality of Vision and Life. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021;226:117-125. 10. Data on file. STAAR Surgical Annual Report.
이보 ICL이란? - 광고심의필: 조합-2022-04-031 (유효기간: 2025.02.07)
1. Feingold et al. Biocompatible, optically transparent, ultraviolet light absorbing, polymeric material based upon collagen and method of making. USPTO June 8, 1999. 2. ICL in Treatment of Myopia (ITM) Study Group. Postoperative Inflammation after Implantation of the Implantable Contact Lens. Ophthalmology 2003;110:2335-2341. 3. Risto J. Uusitalo, et al. Implantable contact lens for high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg 2002(28):29-36. 4. Gregory D. Parkhurst, et al. Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantation in United States Military Warfighters: A Retrospective Analysis of Early Clinical Outcomes of the EVO ICL. J Refract Surg. 2011;27(7);473-481. 5. FDA. Before, During & After Surgery. https://www.fda.gov/medical-de... (as of 2021-12-24) 6. 윤재문 외. 난시교정용 후방 유수정체 안내렌즈 삽입술의 단기간 임상성적. 대한안과학회지. 2009;50(6):839-851. 7. Steven Schallhorn, MD et al. Night Driving Simulation in a Randomized Prospective Comparison of Visian Toric Implantable Collamer Lenses and Conventional PRK for Moderate to High Myopic Astigmatism. Journal of Refractive Surgery Vol.26, No. 5, 2010:321-326. 8. Gregory D Parkhurst. A prospective comparison of phakic collamer lenses and wavefront-optimized laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis for correction of myopia. Clinical Ophthalmology 2016;10:1209-1215. 9. Donald R Sanders et al. United States Food and Drug Administration Clinical Trial of the Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL) for Moderate to High Myopia Three-Year Follow-up. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:1683–1692.
이보 ICL의 장점(야간시력 개선) - 광고심의필: 조합-2022-04-032 (유효기간: 2025.02.07)
1. Steven Schallhorn, MD et al. Night Driving Simulation in a Randomized Prospective Comparison of Visian Toric Implantable Collamer Lenses and Conventional PRK for Moderate to High Myopic Astigmatism. Journal of Refractive Surgery Vol.26, No. 5, 2010:321-326. 2. Gregory D Parkhurst. A prospective comparison of phakic collamer lenses and wavefront-optimized laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis for correction of myopia. Clinical Ophthalmology 2016;10:1209-1215. 3. Donald R Sanders et al. United States Food and Drug Administration Clinical Trial of the Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL) for Moderate to High Myopia Three-Year Follow-up. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:1683–1692. 4. FDA. Before, During & After Surgery. https://www.fda.gov/medical-de... (as of 2021-12-24) 5. 윤재문 외. 난시교정용 후방 유수정체 안내렌즈 삽입술의 단기간 임상성적. 대한안과학회지. 2009;50(6):839-851.
이보 ICL의 장점(안구건조증이 걱정되세요?) - 광고심의필: 조합-2022-04-033 (유효기간: 2025.02.08)
1. Gregory D. Parkhurst, et al. Phakic Intraocular Lens Implantation in United States Military Warfighters: A Retrospective Analysis of Early Clinical Outcomes of the EVO ICL. J Refract Surg. 2011;27(7);473-481. 2. FDA. Before, During & After Surgery. https://www.fda.gov/medical-de... (as of 2021-12-24). 3. 윤재문 외. 난시교정용 후방 유수정체 안내렌즈 삽입술의 단기간 임상성적. 대한안과학회지. 2009;50(6):839-851.
이보 ICL의 장점(마치 내 눈 같은 편안함) - 광고심의필: 조합-2022-04-029 (유효기간: 2025.02.03)
1. FDA. Before, During & After Surgery. https://www.fda.gov/medical-de... (as of 2021-12-24). 2. 윤재문 외. 난시교정용 후방 유수정체 안내렌즈 삽입술의 단기간 임상성적. 대한안과학회지. 2009;50(6):839-851.
수술 과정 - 광고심의필: 조합-2022-04-034 (유효기간: 2025.02.03)
1. FDA. Before, During & After Surgery. https://www.fda.gov/medical-de... (as of 2021-12-24) 2. 윤재문 외. 난시교정용 후방 유수정체 안내렌즈 삽입술의 단기간 임상성적. 대한안과학회지. 2009;50(6):839-851. 3. Elena Martines-plaze, et al. Effect of the EVO + Visian Phakic Implantable Collamer Lens on Visual Performance and Quality of Vision and Life. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021;226:117-125. 4. Data on file. STAAR Surgical Annual Report.
자주 묻는 질문 - 광고심의필: 조합-2022-04-035 (유효기간: 2025.02.03)
1. Feingold et al. Biocompatible, optically transparent, ultraviolet light absorbing, polymeric material based upon collagen and method of making. USPTO June 8, 1999. 2. ICL in Treatment of Myopia (ITM) Study Group. Postoperative Inflammation after Implantation of the Implantable Contact Lens. Ophthalmology 2003;110:2335-2341. 3. Risto J. Uusitalo, et al. Implantable contact lens for high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg 2002(28):29-36. 4. Elena Martines-plaze, et al. Effect of the EVO + Visian Phakic Implantable Collamer Lens on Visual Performance and Quality of Vision and Life. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021;226:117-125.
개인정보 수집 및 이용
이보 ICL 브로슈어 발송을 위한 최소한의 개인정보를 수집하고 이용합니다.
수집된 정보는 이메일 발송 외 다른 목적으로 이용되지 않으며, 서비스가 종료되거나 구독을 해지할 경우 즉시 파기됩니다.